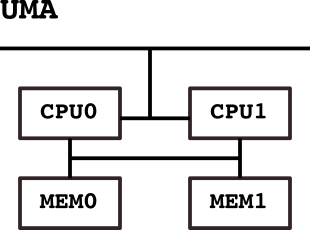
The Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) is a design specification of some modern multiprocessing architectures that are characterized by the fact that not all memory can be access equally from all CPUs in contrast to Uniform Memory Access (UMA). Usually the is due to the fact that each CPU has some memory attached to it. That do not necessarily mean that this memory can not be access by processes from other CPUs, but accessing the memory has some performance penalty. As creating a NUMA architecture is cheaper but still performs well if the programs is carefully designed, this design is quite popular in High Performance Computing (HPC).

History
| Version | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1.2 | 2022-05-17 | Change shell blocks to bash block, history, dots |
| description, Debian helper tools table, +lscpu | ||
| Update for Debian 11 Bullseye | ||
| 0.1.1 | 2020-05-01 | Update for Debian 10 Buster |
| 0.1.0 | 2016-03-24 | Initial release |
Installing
The content of installation varies. It is recommended to either use a new distribution or even compile numactl from source, as this also includes the numademo command.
Installing Numa Helper Tools For Debian
| Package | Stretch 9.12 | Buster 10 | Bullseye 11 |
|---|---|---|---|
| numactl | 2.0.11-2.1 | 2.0.12-1 | 2.12-1+b1 |
| numad | 0.5+20150602-5 | 0.5+20150602-5 | 0.5+20150602-7 |
| numatop | 1.0.4-3 | 2.1-2 | 2.1-4 |
| util-linux | 2.29.2-1+deb9u1 | 2.33.1-0.1 | 2.36.1-8+deb11u1 |
| Command | Package | Source |
|---|---|---|
| lscpu | util-linux | util-linux |
| memhog | numactl | numactl |
| numastat | numactl | numactl |
| migspeed | numcatl | numactl |
| migratepages | numactl | numactl |
| numademo | n.a. | numactl |
| numatop | numatop | numatop |
| numad | numad | numad |
numademois part ofnumactlbut not packaged
lscpu
The tool lscpu can be used to understand the number of NUMA nodes.
# Laptop 2008
lscpu|grep NUMA
NUMA node(s): 1
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0,1
# Desktop 2015
lscpu|grep NUMA
NUMA node(s): 1
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
# Raspberry Pi 4
lscpu|grep NUMA
NUMA node(s): 1
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3
# Server 2022
lscpu|grep NUMA
NUMA node(s): 1
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-11Standard hardware not used for HPC usually only have one NUMA node. Typical X86 NUMA hardware has 2 or more CPUs and 2 or more memory banks, one attached to each CPU.
Compiling And Installing numactl From Source
aptitude install autoconf automake
git clone https://github.com/numactl/numactl.git
cd numctl
./autogen.sh
./configure
make
make installNumactl Commands
migratepages
The man pages says: “migratepages moves the physical location of a processes pages without any changes of the virtual address space of the process. Moving the pages allows one to change the distances of a process to its memory. Performance may be optimized by moving a processes pages to the node where it is executing.”
numastat
The numastat command shows per-NUMA statistics for processes and the operating system.
Example for one CPU:
numastat
node0
numa_hit 366309
numa_miss 0
numa_foreign 0
interleave_hit 7846
local_node 366309
other_node 0numactl
The numactl command controls the NUMA policy for processes or shared memory.
Example for one CPU:
numactl --show
policy: default
preferred node: current
physcpubind: 0 1 2 3 4 5
cpubind: 0
nodebind: 0
membind: 0
numactl --hardware
available: 1 nodes (0-0)
node 0 size: 6025 MB
node 0 free: 5612 MB
node distances:
node 0
0: 10memhog
The memhog command allocates memory with a policy for testing. For some reasons the Debian 10 Buster version do not include a man page. However there is a page online.
Allocate a 1G region, (implicit) default policy, repeat test 4 times
memhog -r4 1G
...............................................................................
...............................................................................
...............................................................................
...............................................................................numademo
The command numademo is not available via Debian package, it is available via numctl source code.
On an old laptop from 2008 with Debian 8.11 Jessie (used with a compiled numademo executable from numactl source from before 2020, maybe in 2016):
./numademo -S 100M
1 nodes available
memory with no policy memset Avg 2304.98 MB/s Max 2310.25 MB/s ...
local memory memset Avg 2302.23 MB/s Max 2310.05 MB/s ...
memory interleaved on all nodes memset Avg 2295.28 MB/s Max 2307.35 MB/s ...
memory on node 0 memset Avg 2303.58 MB/s Max 2306.69 MB/s ...
[...]Executing this test on Debian 11 Bullseye on a desktop from 2013 or a laptop from 2015 or on the same laptop from 2008 (Debian 8.11 Jessie) the newer version gives:
/numademo -S 100M
A minimum of 2 nodes is required for this test.It seems that the minimum requirement for the test changed.
Numatop
This tool require a supported CPU. If executed on non supported CPU it will state that:
numatop -s low -l 2 -f /tmp/warn.log
CPU is not supported!